BGP Virtual IP
Jadi goals riset ini adalah bagaimana caranya membuat sebuah virtual ip yang bisa di reach oleh network kvm.

Refrensi : https://docs.vultr.com/high-availability-on-vultr-with-floating-ip-and-bgp
Jadi goals riset ini adalah bagaimana caranya membuat sebuah virtual ip yang bisa di reach oleh network kvm. VirtualIP disini masih belum sempurna, karena beberapa kali pengetestan dan tuning buat pindah ke vm lain masih terdapat jeda yang sangat lumayan > 1 menit.
environment
Pakai OS Ubuntu 22.04 Server
| VM Hostname | IP |
|---|---|
| rke-server-01 | 10.10.11.10 |
| rke-server-02 | 10.10.11.11 |
| rke-server-03 | 10.10.11.12 |
| vip-rke | 10.10.11.100 |
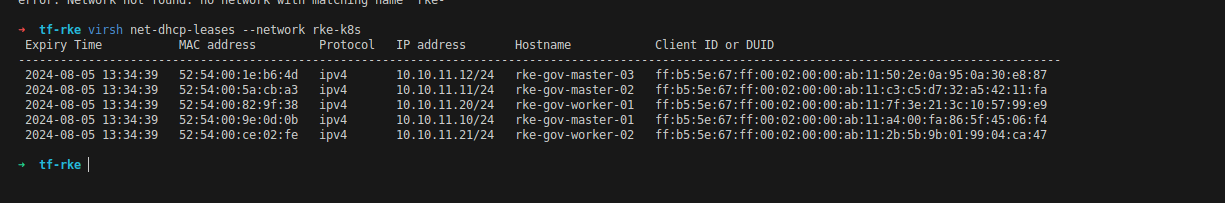
Kondisi awalnya terlihat kalau tidak terdapat ip 10.10.11.100 di dhcp-leases. |
|
 |
|
 |
|
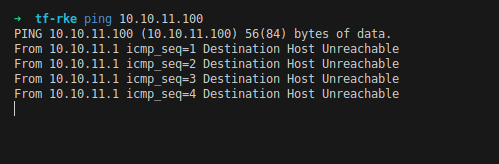
| Di ping juga pastinya engga mau, karena belum di setup |
Setup
Exec on all node
- Install bird
sudo apt install bird
- Add virtual ip di interface loopback.
sudo vim /etc/netplan/xx.yaml
network:
ethernets:
lo:
addresses:
- 127.0.0.1/8
- ::1/128
- 10.10.11.100/32
sudo netplan apply
Pastikan interface lo memiliki virtualip
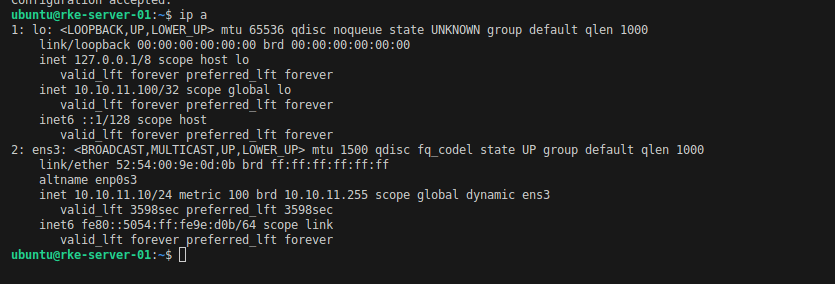
config rke-server-01
sudo vim /etc/bird/bird.conf
# This is a minimal configuration file, which allows the bird daemon to start
# but will not cause anything else to happen.
#
# Please refer to the documentation in the bird-doc package or BIRD User's
# Guide on http://bird.network.cz/ for more information on configuring BIRD and
# adding routing protocols.
# Change this into your BIRD router ID. It's a world-wide unique identification
# of your router, usually one of router's IPv4 addresses.
router id 10.10.11.10;
# The Kernel protocol is not a real routing protocol. Instead of communicating
# with other routers in the network, it performs synchronization of BIRD's
# routing tables with the OS kernel.
protocol kernel {
scan time 60;
import none;
# export all; # Actually insert routes into the kernel routing table
}
# The Device protocol is not a real routing protocol. It doesn't generate any
# routes and it only serves as a module for getting information about network
# interfaces from the kernel.
protocol device {
scan time 60;
}
protocol direct {
interface "lo";
}
protocol bgp uplink_1 {
local as 64512;
source address 10.10.11.10;
import none;
export all;
graceful restart on;
neighbor 10.10.11.11 as 64512;
}
protocol bgp uplink_2 {
local as 64512;
source address 10.10.11.10;
import none;
export all;
graceful restart on;
neighbor 10.10.11.12 as 64512;
}
Enable bird
sudo enable --now bird
config rke-server-02
sudo vim /etc/bird/bird.conf
# This is a minimal configuration file, which allows the bird daemon to start
# but will not cause anything else to happen.
#
# Please refer to the documentation in the bird-doc package or BIRD User's
# Guide on http://bird.network.cz/ for more information on configuring BIRD and
# adding routing protocols.
# Change this into your BIRD router ID. It's a world-wide unique identification
# of your router, usually one of router's IPv4 addresses.
router id 10.10.11.11;
# The Kernel protocol is not a real routing protocol. Instead of communicating
# with other routers in the network, it performs synchronization of BIRD's
# routing tables with the OS kernel.
protocol kernel {
scan time 60;
import none;
# export all; # Actually insert routes into the kernel routing table
}
# The Device protocol is not a real routing protocol. It doesn't generate any
# routes and it only serves as a module for getting information about network
# interfaces from the kernel.
protocol device {
scan time 60;
}
protocol direct {
interface "lo";
}
protocol bgp uplink_1 {
local as 64512;
source address 10.10.11.11;
import none;
export all;
graceful restart on;
neighbor 10.10.11.10 as 64512;
}
protocol bgp uplink_2 {
local as 64512;
source address 10.10.11.11;
import none;
export all;
graceful restart on;
neighbor 10.10.11.12 as 64512;
}
Enable service bird
sudo systemctl enable --now bird
config rke-server-03
sudo vim /etc/bird/bird.conf
# This is a minimal configuration file, which allows the bird daemon to start
# but will not cause anything else to happen.
#
# Please refer to the documentation in the bird-doc package or BIRD User's
# Guide on http://bird.network.cz/ for more information on configuring BIRD and
# adding routing protocols.
# Change this into your BIRD router ID. It's a world-wide unique identification
# of your router, usually one of router's IPv4 addresses.
router id 10.10.11.12;
# The Kernel protocol is not a real routing protocol. Instead of communicating
# with other routers in the network, it performs synchronization of BIRD's
# routing tables with the OS kernel.
protocol kernel {
scan time 60;
import none;
# export all; # Actually insert routes into the kernel routing table
}
# The Device protocol is not a real routing protocol. It doesn't generate any
# routes and it only serves as a module for getting information about network
# interfaces from the kernel.
protocol device {
scan time 60;
}
protocol direct {
interface "lo";
}
protocol bgp uplink_1 {
local as 64512;
source address 10.10.11.12;
import none;
export all;
graceful restart on;
neighbor 10.10.11.10 as 64512;
}
protocol bgp uplink_2 {
local as 64512;
source address 10.10.11.12;
import none;
export all;
graceful restart on;
neighbor 10.10.11.11 as 64512;
}
Enable service bgp
sudo enable --now bird
Verifikasi
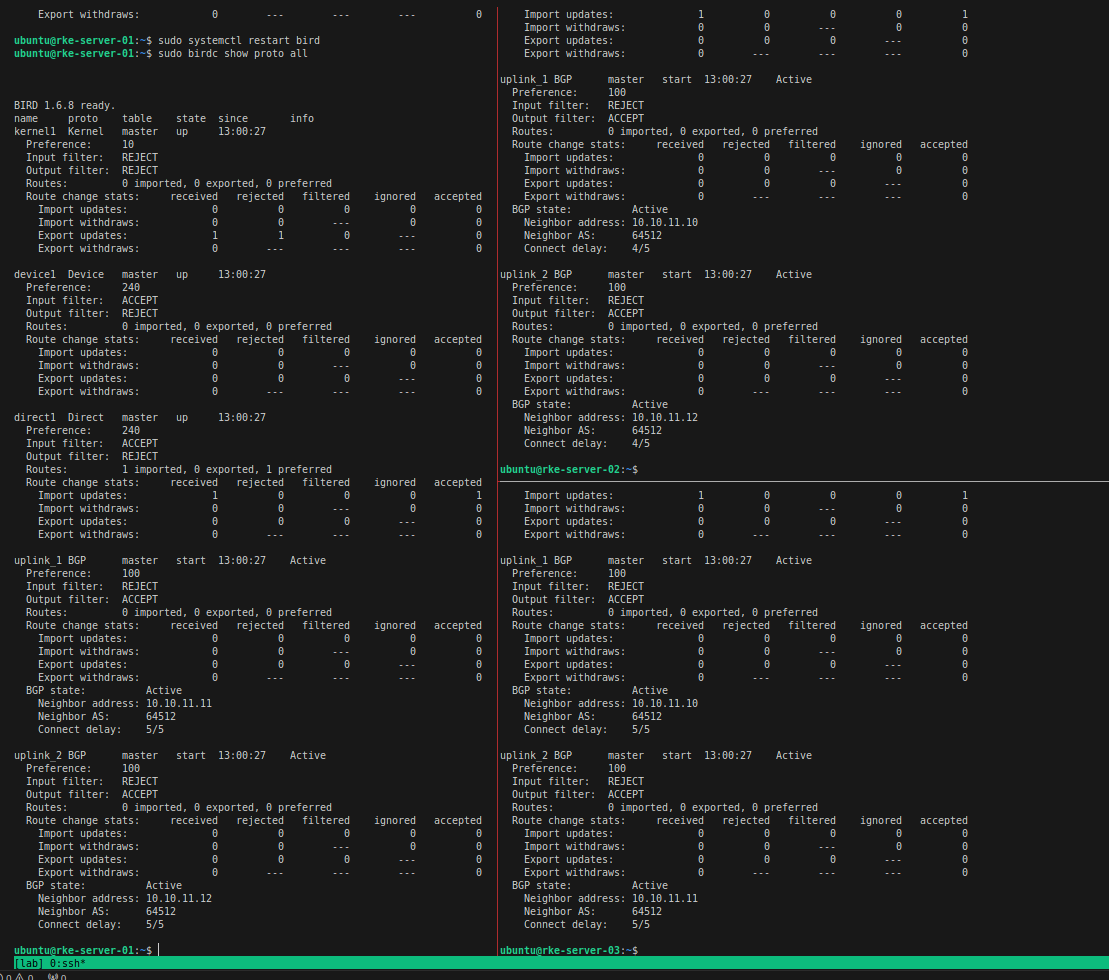
- Check bgp session tiap vm
birdc show proto all
Pastikan bgp state udah Active
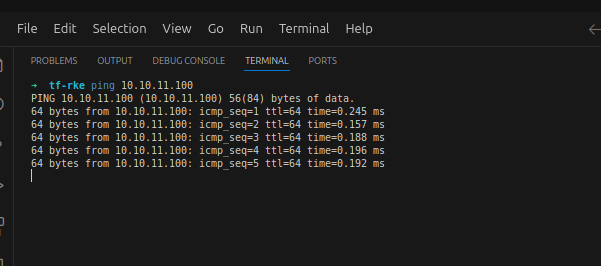
- Ping vip dari baremetal
- Install nginx masing", dan ubah index dengan hostname. Dan curl dari baremetal
curl 10.10.11.100
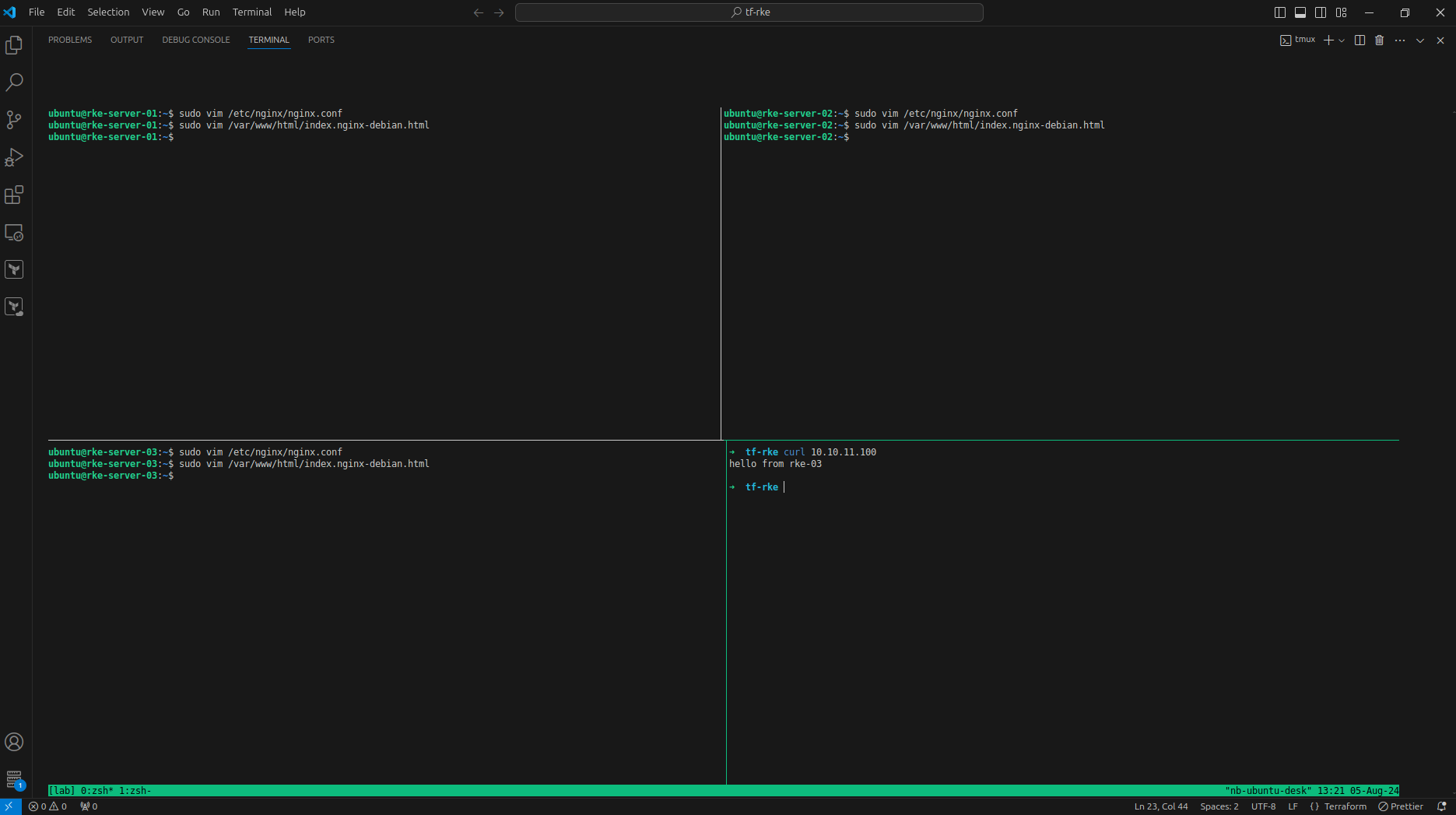
Coba curl terus menerus, sambil matikan instance rke-3
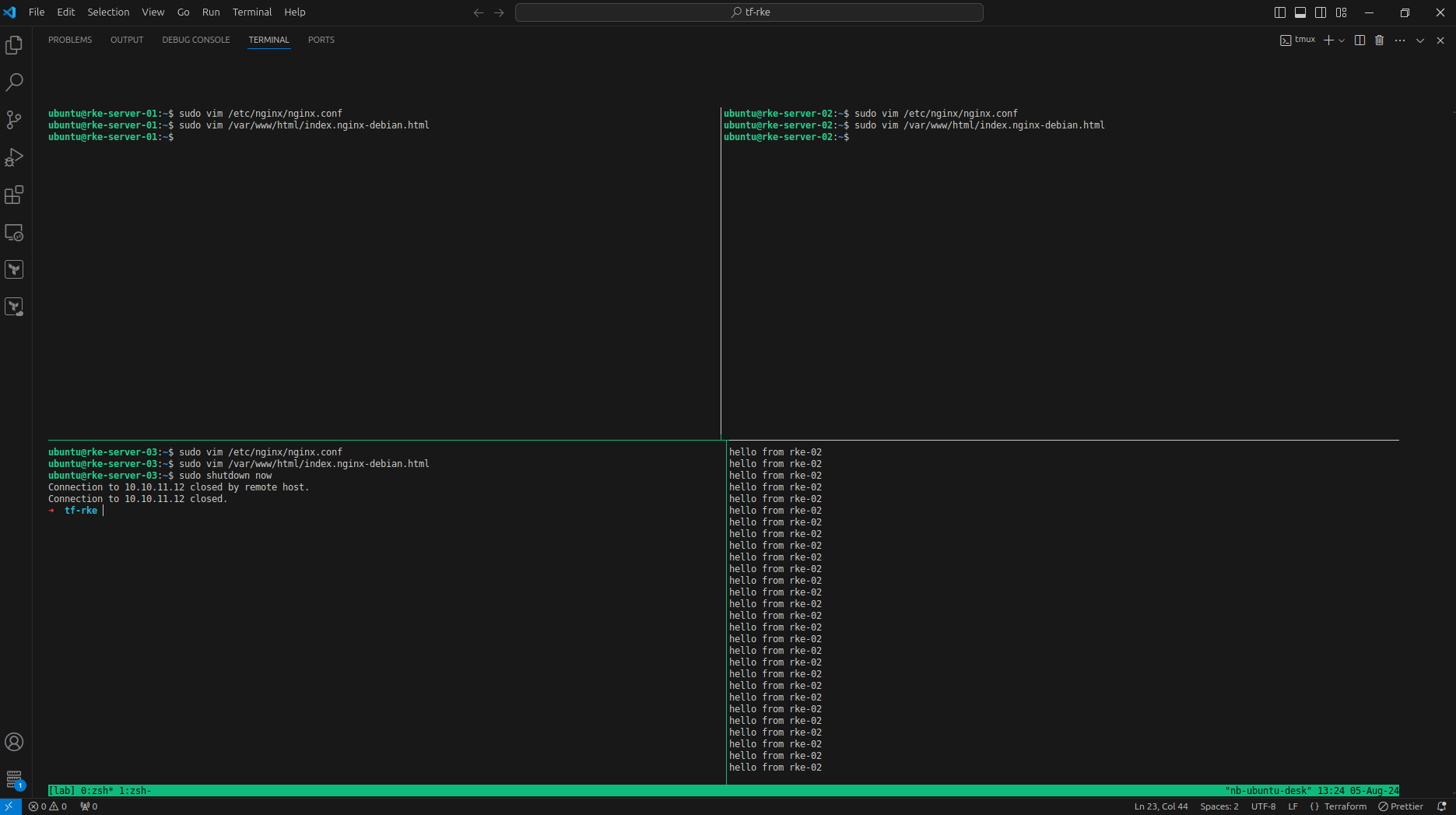
Dan ip berpindah ke rke-2. perpindahan cukup lama, dan memang bgp sepertinya tidak bestpractice sebagai vrrp dibandingkan keepalive.




